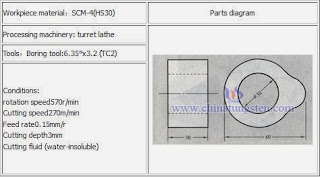
Cemented carbide tool cutting edge defect and honing (The outer periphery cutting of vehicle parts)
Cemented carbide tool cutting edge defect and honing (The outer periphery cutting of vehicle parts)Results: cemented carbide cutting edge defect occurs, the life will be shortened. Cemented carbide tool cutting edge honing can increase tool life
Summary: In general, cutting steel when necessary to carry out the cutting edge honing of cemented carbide tool, cemented carbide cutting edge honing can prevent the fragmentation of the cutting edge and glue attachments cutting edge processing, or due to the cutting the vibration generated by the chipping, and the gap. Honed width of the cemented carbide cutting edge is approximately 0.5-0.8 times the feed amount.